Cell Differentiation Studies
Independent studies utilizing the Australian patented ultrasonication protocol to obtain Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) demonstrate cell viability (live cells) and differentiation.
Independent studies have validated Cell-Innovations ultrasonication protocol to obtain viable, adherent cells capable of mitotic division and differentiation. There were no differences between collagenase digestion and Cell-Innovations ultrasonication protocol in terms of cell population doubling time, freeze-thaw viability, or differentiation into either bone or adipose tissues.
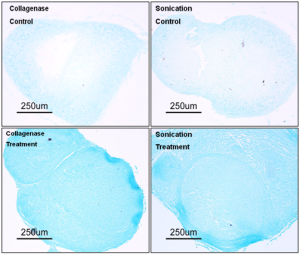
The old methods of collagenase separation of adipose to SVF are shown below in comparison to ultrasonication separation of SVF in the University study below.
Viability of cells from adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF)
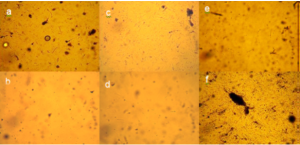
Adipose-derived SVF after 5 days in culture at 40x magnification are adherent. Images obtained of cells isolated from patients using collagenase correspond to: a, c, and e, respectively. Images obtained of cells isolated from patients using ultrasonication correspond to: b, d, and f, respectively
Differentiation of cells obtained by the ultrasonication protocol
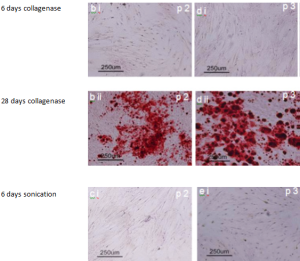
Osteoblastic (bone) differentiation of cells are typically tested by staining with Alizarin red which indicates calcium-rich deposits.
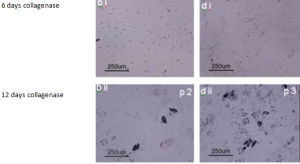
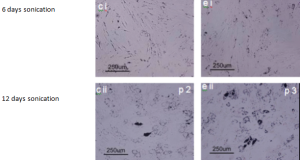
Adipose-derived SVF cells cultured in osteogenic media for 28 days (bii- eii) or control media for 6 days (bi- ei) from patients and stained with alizarin red. The stain alizarin red Images at 100x magnification. Images b, and d were obtained from cells isolated using collagenase method. Images c, and e were obtained from cells isolated using ultrasonication.
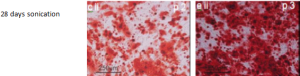
Adipogenic (fat cell). Differentiation of cells into adipocytes (fat) are typically tested by staining with Oil Red O which stains triglycerides (intracellular lipid vesicles).
Adipose-derived SVF cultured in adipogenic media for 12 days (bii- e ii) or control media for 6 days (bi- ei) from patients and stained with oil red o. Images at 100x magnification. Images b, and d were obtained from cells isolated using collagenase method. Images c, and e were obtained from cells isolated using ultrasonication.
 Chondrogenic (cartilage) differentiation of cells results in formation of cartilage with a typical extracellular matrix. A key molecule besides collagen type II within this extracellular matrix is the proteoglycan aggrecan. Alcian Blue a blue copper containing dye can detect aggrecan an indicator of cartilage formation.
Chondrogenic (cartilage) differentiation of cells results in formation of cartilage with a typical extracellular matrix. A key molecule besides collagen type II within this extracellular matrix is the proteoglycan aggrecan. Alcian Blue a blue copper containing dye can detect aggrecan an indicator of cartilage formation.